This page is just a loose collection, of mostly high-level \ early p2p history. A little further down, you’ll find a site directory. However, it’s structured so that you should be able to simply scroll through the posts, and generally progress forward through history.
Of course it took a bit of fiddling about with the publish date to achieve this effect, but I think it was worth the effort.
Internet-based peer-to-peer networks became popular in the 1990s due to the development of P2P file-sharing networks such as Napster. Technically, many P2P networks are not pure peer networks but rather hybrid designs as they utilize central servers for some functions such as search.
gdamdam/awesome-decentralized-web
P2P and Decentralized Web Histories
- P2P Foundation
- Definition of P2P
- A Brief History of Peer to Peer Netowrks
- Limewire, Napster, The Pirate Bay
- Introduction to P2P Networks - Limewire
- A Network of Peers: Peer-to-Peer Models Through the History of the Internet
The Internet is a shared resource, a cooperative network built out of millions of hosts all over the world. Today there are more applications than ever that want to use the network, consume bandwidth, and send packets far and wide. Since 1994, the general public has been racing to join the community of computers on the Internet, placing strain on the most basic of resources: network bandwidth. And the increasing reliance on the Internet for critical applications has brought with it new security requirements, resulting in firewalls that strongly partition the Net into pieces. Through rain and snow and congested Network Access Providers (NAPs), the email goes through, and the system has scaled vastly beyond its original design.

Filesharing
- The History of Filesharing
- Timeline of Filesharing
- A Brief History of P2P Content Distribution, in 10 Major Steps
Pre-History
History of Border Gateway Protocol
- ARPANet 1969
- USENET, 1979 - Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)
- Gateway-to-gateway protocol (GGP) 1982 - its only focus was routing based on the number of AS hops. GGP focused on routing internet transit the fewest number of autonomous system (AS) hops to a destination.
- 1984
- FidoNet
- Exterior gateway protocol (originally discussed in 1982) a tree-like distance-vector internet routing protocol.
- Cisco Systems founded
- 1985 - The National Science Foundation begins to support advanced research and education in networking.
- Between the developments of Usenet in 1979 to the 1990’s, files sharing were primarily done through the use of bulletin board based systems.
- 1986 - The first super computers are connected to the internet. The National Science Foundation Network (NSFNET) initiated TCP/IP connections and operations. This becomes the first form of the internet backbone.
- 1988 - Internet routing (BGP) -RFC 1058. This is the oldest distance-vector routing protocol in its modern context. This begins to lay the groundwork for BGP.
- August 1989 - Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
The events through the 1980s expose the need for an all-encompassing internet routing protocol. This is exactly when BGP is developed. On three sheets of paper.
Peer to peer networks can be configured over LAN or the Internet. Local area P2P networks can be configured to be either wired or wireless and allow the sharing of files, printers, and other resources between involved computers. Over the Internet, P2P networks can handle an extremely high volume of file sharing because the workload is distributed across many computers worldwide. Internet based P2P networks are less likely to fail or experience a traffic bottleneck than client-server networks for the same reason.
The basic idea of P2P networking has been around since 1969, when the Internet Engineering Task Force pusblished its first Request for Comments.[4] However, the first dial-up P2P network was created in 1980 in the form of Usenet, which was a worldwide Internet discussion system. The difference between other web forums and Usenet was that Usenet did not depend on a central server or administrator– it was distributed among a constantly changing group of servers that stored and forwarded messages to one another in bursts called news feeds. Individual users could read messages from and post messages to a local server, which would then send posted messages around the world.[5]
Network Control Protocol (NCP)
1970 the ARPANET had its first host-to-host protocol, the Network Control Protocol (NCP)
public demonstration of the ARPANET and its potentials at the International Conference on Computer Communication (ICCC) held in Washington, D.C., in October 1972.
- Internet History Timeline: ARPANET to the World Wide Web
- How the Internet was Born, from Arpanet to the Internet
Related Posts: P2P History
If you feel like jumping around, you can always come back here for the main navigation.
Study Guide: History Computer Communications 1968-1988
1st Gen Centralized - Napster
2nd Gen Decentralized - BitTorrent
3rd Gen Darknets - Freenet
Decentralized Web Summit- 2016 Participating Organizations
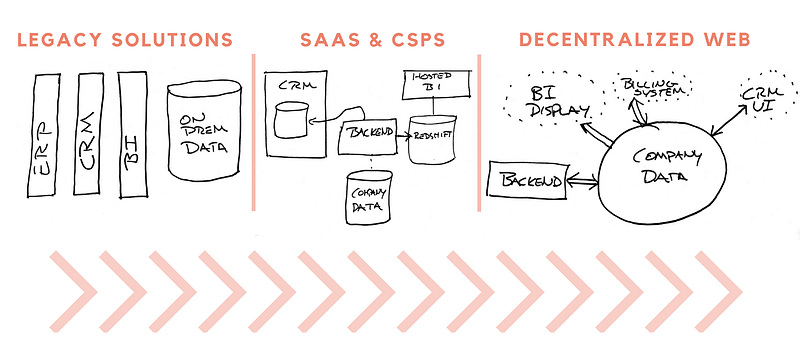
After Bitcoin
- 2009 - Bitcoin
- 2011 - Namecoin
- 2012 - Diaspora
Decentralised Storage Networks
- Filecoin
- Swarm
- Sia
- Storj
- Maidsafe
P2P-Extra
aMule -aMule is a peer to peer file sharing application that works with the eDonkey computer network, but offers more features than the standard eDonkey client. It is based on the eMule sourcecode, and evolved from ?LMule and xMule. It is now the Linux client on the eMule links section on their webpage. As eMule, aMule is open source software released under the GNU ?GeneralPublicLicense.
- emule-project eMule project - or eMule on Sourceforge
- Freemule.net - Website with the latest news on eMule’s legal actions
- amule.org aMule’s homepage - or aMule on ?BerliOS
- wiki.amule.org aMule Wiki- Wiki of the aMule Project